Describe the Differences in the Four Protein Structures
Tertiary structure refers to the three-dimensional structure of an entire polypeptide chain. Primary structure refers to the linear sequence of the amino acids connected by the peptide bonds.

Structure Of Proteins Ck 12 Foundation
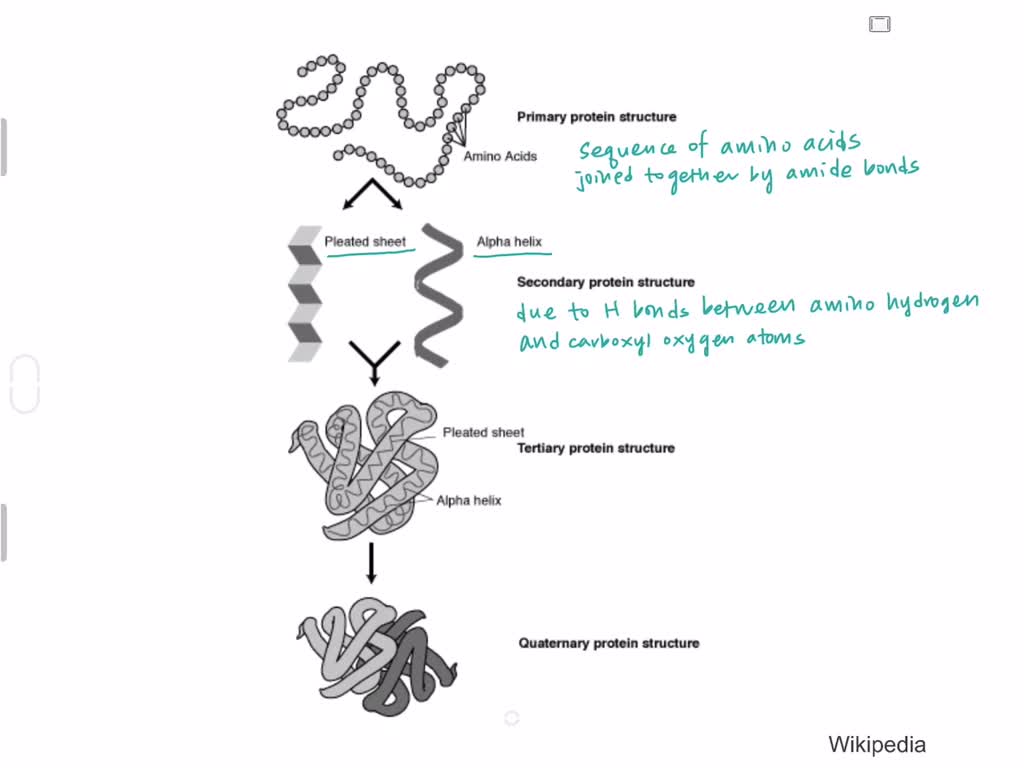
Proteins have four levels of organization.
. An alpha helix goes round and round a beta strand zigs and zags and a few fibrous proteins like alpha-keratin collagen and fibroin ONLY have secondary structure. Hydrogen bonds between polar amino acids ionic bonds covalent bonds between sulphur containing amino acids hydrophobic interactions between non-polar amino acids. Protein structure depends on its amino acid sequence and local low-energy chemical bonds between atoms in both the polypeptide backbone and in amino acid side chains.
The main difference between primary secondary and tertiary structure of protein is that the primary structure of a protein is linear and the secondary structure of a protein can be either an α-helix or β-sheet whereas tertiary structure of a protein is globular. It is the description of basic structure of a protein. Primary secondary tertiary and quaternary are the four structures of proteins found in nature.
Primary structure is the amino acid. The different levels of protein structure are known as primary secondary tertiary and quaternary structure. Primary secondary tertiary and quaternary structure.
The 20 different types of amino acids combines to form numerous types of proteins which confer a unique 3-D structure and performs specific functions. It is convenient to describe protein structure in terms of 4 different aspects of covalent structure and folding patterns. Formed from interactions between R-groups.
There are four types of protein structure. To understand how a protein gets its final shape or conformation we need to understand the four levels of protein structure. Tertiary structure describes all aspects of the three-dimensional folding of a polypeptide.
And quaternary structure is the three-dimensional arrangement of the subunits in a. Explain what happens if even one amino acid is substituted for another in a polypeptide chain. B The secondary structure is the 3-D arrangement of the right-handed alpha helix shown here or.
Give the name of the fourth protein structure and what makes it. Proteins are complex organic compounds which is made up of considerable amount of smaller units of amino acids. Primary structure Each protein is built up from a set number of amino acids joined and shaped in a particular way.
The four levels of protein structure are distinguished from one another by the degree of complexity in the polypeptide chain. Protein structure plays a key role in its function. These include primary structure secondary structure tertiary structure and quaternary structure.
A single protein molecule may contain one or more of the protein structure types. Describe the differences in the four protein structures. Primary structure is the amino acid sequence.
The following points highlight the four main structures of Protein Organisation. A proteins primary structure is defined as the amino acid sequence of its polypeptide chain. Made of 2 or more polypeptides.
There are four types of protein structure. The secondary structure consists of local packing of polypeptide chain into α-helices and β-sheets due to hydrogen bonds between peptide bond central carbon backbone. Primary structure The simplest level of protein structure primary structure is simply the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain.
A single protein molecule may contain one or more of the protein structure types. Biochem Exam 2 chapter 3B 47 terms. These include primary structure secondary structure.
Secondary structure refers to stable structural patterns of the peptide chains. Differentiate the four types of protein structure. Primary Structure of Proteins.
8000 combinations for a tripeptide. There are 20 different types of amino acids so for a simple dipeptide there are 400 possible combinations. Secondary structure is the local spatial arrangement of a polypeptides backbone main chain atoms.
Aquaporins are proteins embedded in the plasma membrane that allow water molecules to move between. If a protein loses its shape at any structural level it may no longer be functional. The amino acid sequence in the peptide chains of the protein and the bonding between them -like peptide hydrogen sulphide describe the primary structure.
Primary secondary tertiary and quaternary. The four levels of protein structure are distinguished from one another by the degree of complexity in the polypeptide chain. Four levels of Protein Structure a The primary structure is the succession of amino acid residues usually abbreviated by the 1- or 3-letter codes.
Clearly the number of possible combinations is almost infinite when larger numbers of amino acids are combined to form a.

Protein Structure Biology Dictionary

Protein Structure Introduction To Chemistry
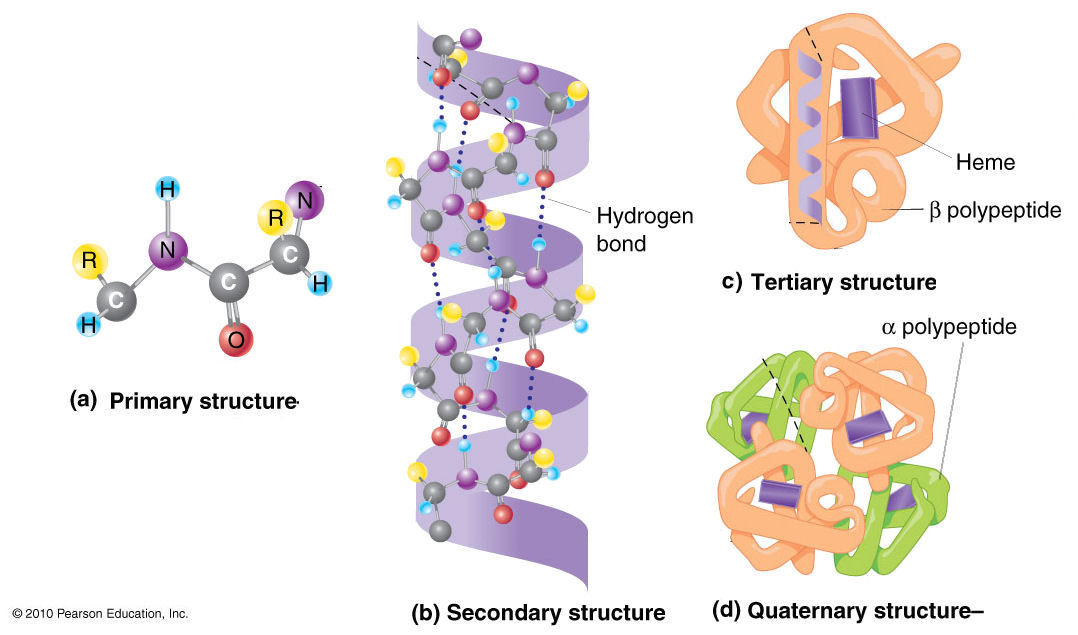
Four Levels Of Protein Structure

Solved Describe The Differences In The Four Protein Structures
No comments for "Describe the Differences in the Four Protein Structures"
Post a Comment